-40%
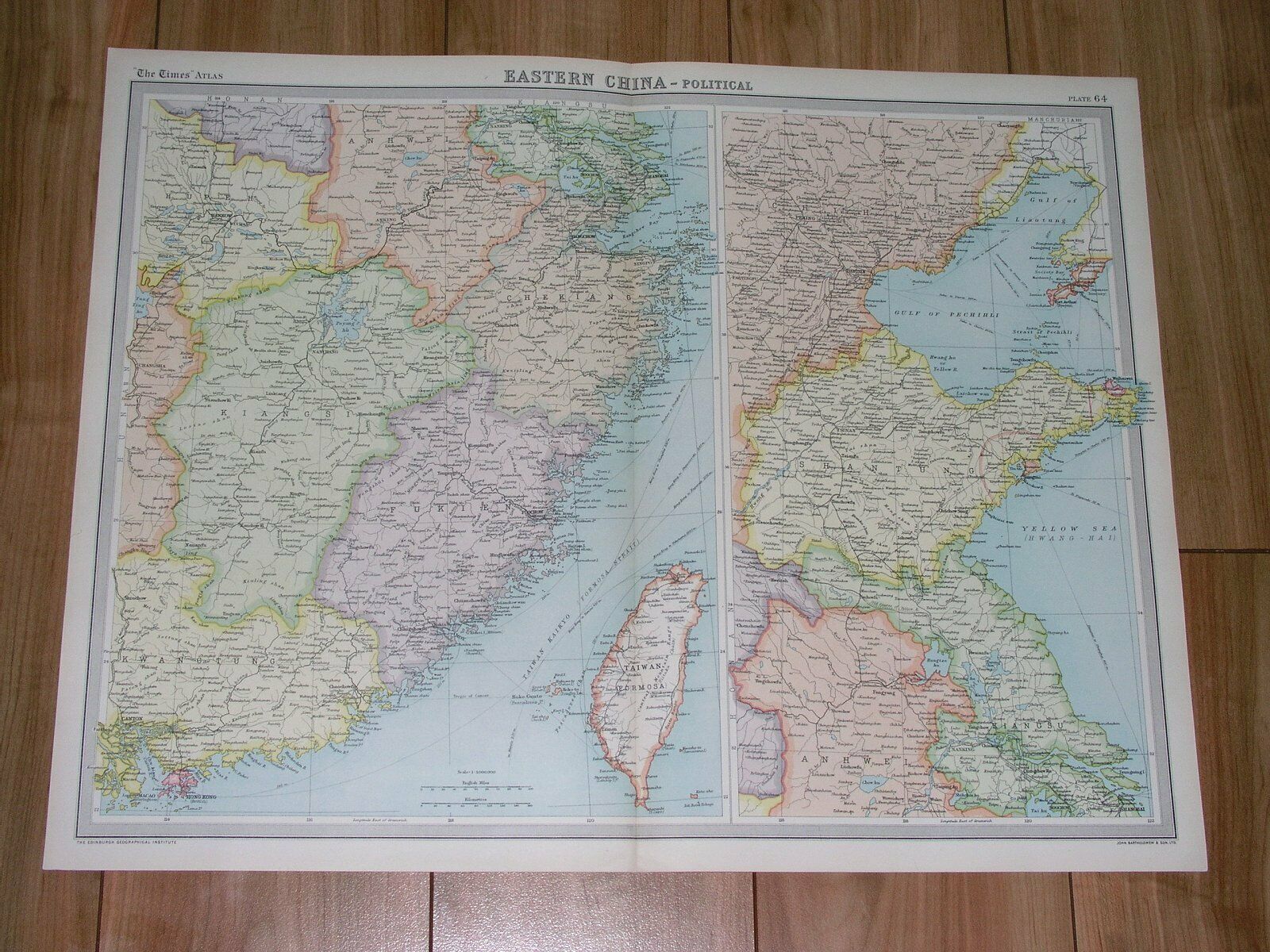
1882 Perron map ULAN BATOR, MONGOLIA (#39)
$ 10.53
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Perron07_0391882 Perron map ULAN BATOR, MONGOLIA (#39)
Nice little map titled
Ourga
,
from wood engraving with fine detail and clear impression, nice hand coloring. Overall size approx. 17 x 15.5 cm, image size approx. 11 x 8 cm. From
La Nouvelle Géographie universelle, la terre et les hommes
, 19 vol. (1875-94), great work of Elisee Reclus. Cartographer is Charles Perron.
Ulaanbaatar
also spelled Ulan Bator , formerly Urga or Niislel Khureheh
capital and largest city of Mongolia. It is situated on the Tuul River on a windswept plateau at an elevation of 4,430 feet (1,350 m). The city originated as a seasonal migratory abode of the Mongolian princes and in 1639 finally attained permanence on the present site with the construction of Da Khure Monastery. This building became the residence of the bodgo-gegen, high priest of the Tibetan Buddhist religion (to which the Mongols adhere), and remained as such for about 200 years. Da Khure became known to the Russians as Urga and developed as a trade centre between China and Russia. In 1911, when Outer Mongolia declared itself independent, the city was renamed Niislel Khureheh (“Capital of Mongolia”). In 1921 it was occupied by troops of Mongolia's revolutionary leader, Damdiny Sühbaatar, and the Soviet Red Army. When Mongolia was declared a people's republic in 1924, the city was renamed Ulaanbaatar, which means “Red Hero.”
With Soviet help, a new city was planned, and its central feature was Sühbaatar Square, site of a Neoclassic government building, a history museum, and the national theatre. The city is also the site of the National University of Mongolia (1942), several professional and technical schools, and the Academy of Sciences of Mongolia.
Ulaanbaatar is the main industrial centre of Mongolia. An industrial complex produces a variety of consumer goods. There are cement, iron, and brick works; footwear and garment factories; vehicle-repair works; food-processing plants; and other factories. A railroad and an international airport connect the city with China and Russia. The scenic wooded peaks of the Hentiyn Mountains extend to the northeast of the city. Pop. (2000) 760,077; (2007 est.) 1,031,200.